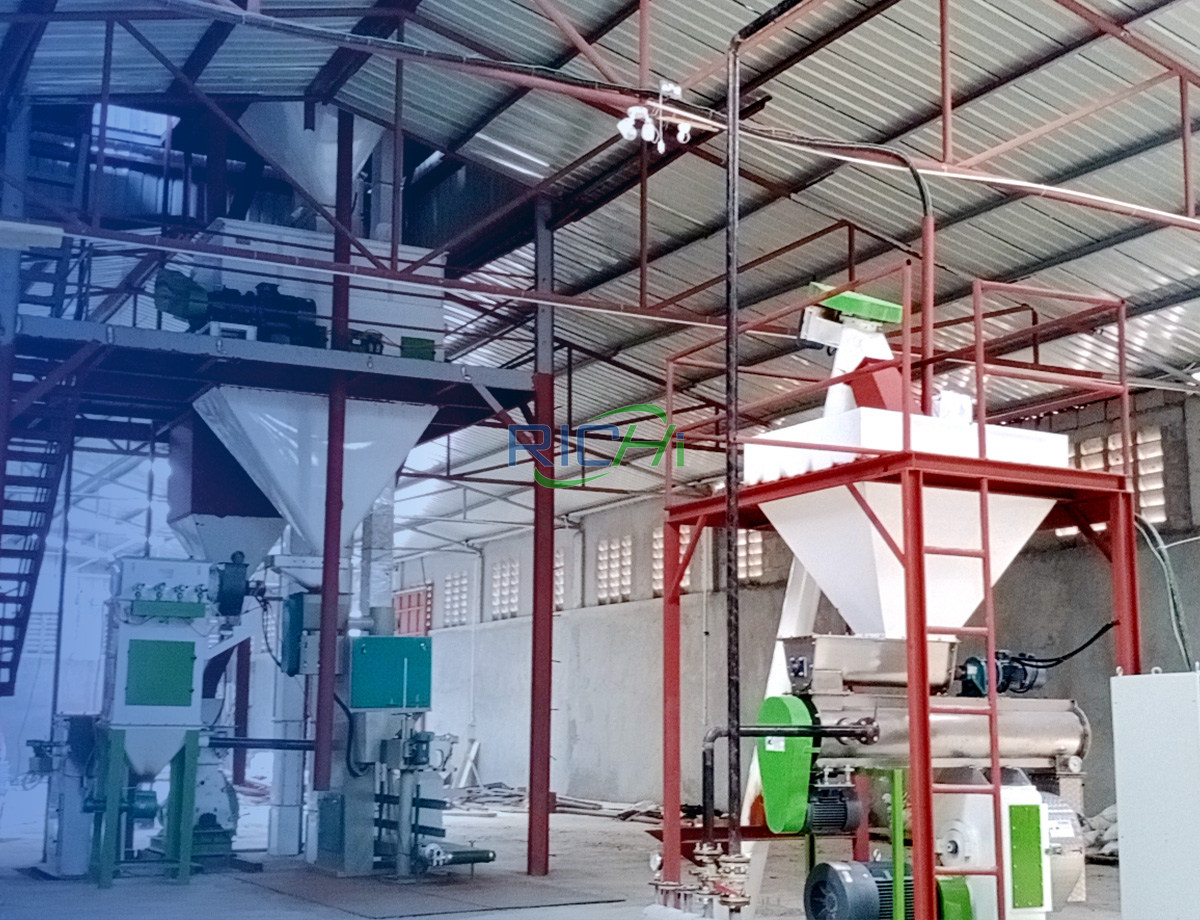
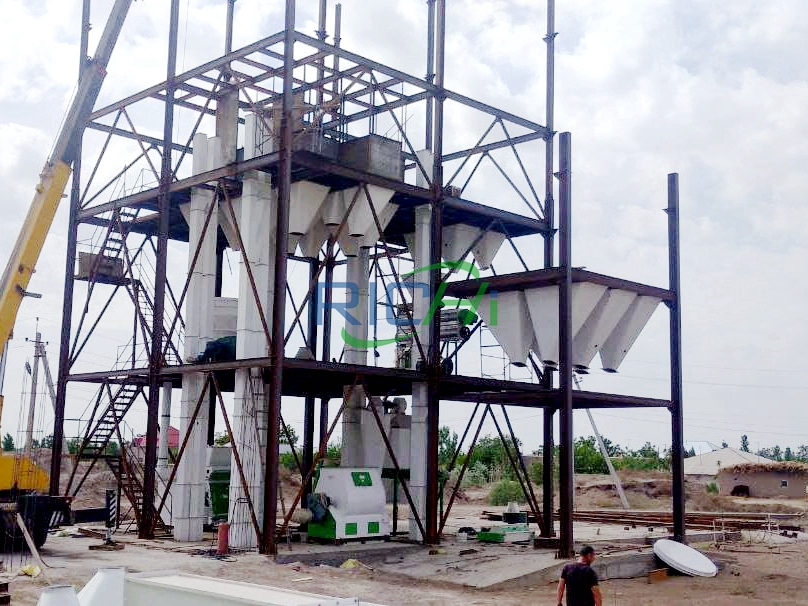
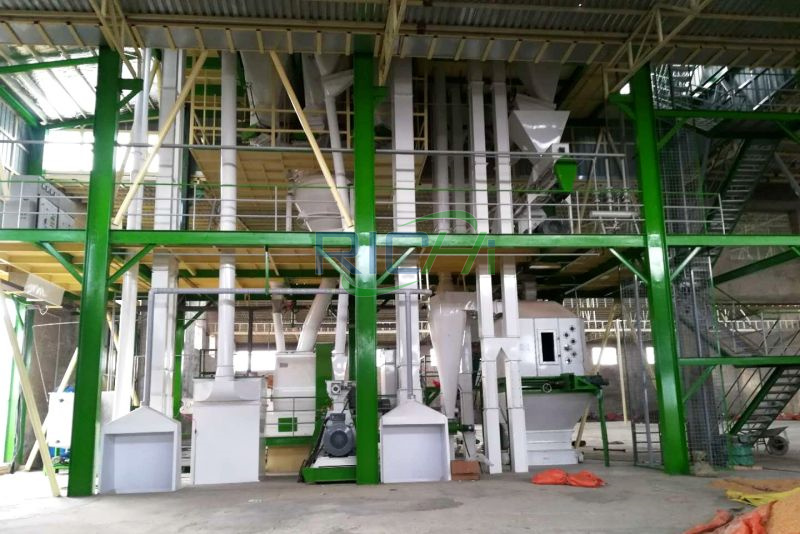
The production of animal feed is a vital aspect of the agricultural industry, ensuring that livestock receive the necessary nutrients for growth and productivity. A 3-4 tons per hour (t/h) animal feed production machine is designed to meet the needs of small to medium-scale operations, providing flexibility and efficiency in feed manufacturing. This article outlines the main equipment involved in a 3-4 t/h animal feed production line and discusses the functions and importance of each component.
1. Raw Material Reception and Cleaning Equipment
The first step in the feed production process involves receiving and cleaning raw materials to ensure high-quality feed.
- Receiving Hoppers: These are used to receive bulk raw materials such as grains, soybeans, and other ingredients. They are designed to handle large volumes and facilitate the efficient transfer of materials into the production line.
- Cleaning Machines: Cleaning equipment, such as vibrating screens and magnetic separators, is essential for removing impurities, dust, and foreign materials from the raw ingredients. This step is crucial to prevent contamination and ensure the quality of the final product.
2. Grinding Equipment
After cleaning, the raw materials must be ground to the appropriate particle size for mixing and pelleting.
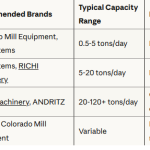
- Hammer Mill: The hammer mill is a common piece of equipment used for grinding grains and other ingredients. It uses rotating hammers to crush the materials into smaller particles, achieving the desired consistency. The particle size is critical for ensuring uniform mixing and effective pelleting.
- Roller Mill: In some cases, a roller mill may be used instead of a hammer mill. Roller mills are particularly effective for grinding grains into finer particles while preserving the nutritional value of the ingredients.
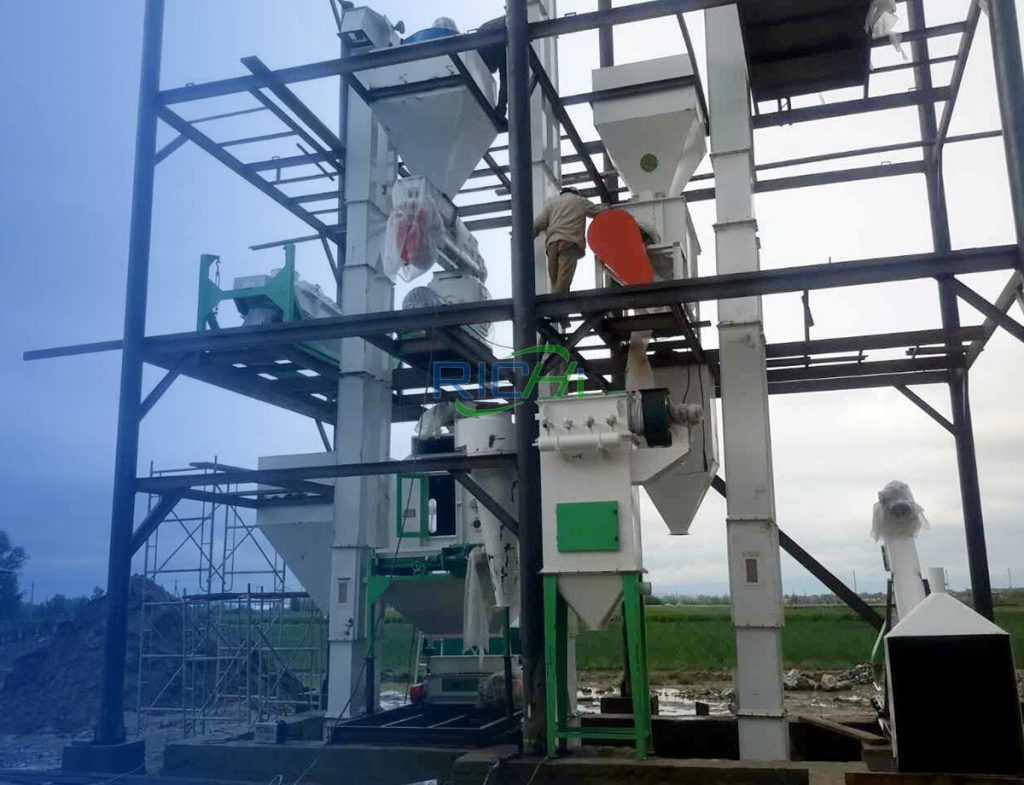

3. Mixing Equipment
Once the raw materials are ground, they need to be thoroughly mixed to ensure uniform distribution of nutrients.
- Horizontal Mixer: A horizontal mixer is commonly used in animal feed production. It consists of a horizontal trough with mixing blades that ensure even blending of the ingredients. The mixer can handle both dry and wet ingredients, making it versatile for various formulations.
- Batching System: An automated batching system can be integrated with the mixer to accurately measure and dispense the required amounts of each ingredient. This ensures consistency in feed formulations and reduces the risk of errors.
4. Conditioning Equipment
Conditioning is a critical step that prepares the feed mixture for pelleting by improving its moisture content and temperature.
- Steam Conditioner: A steam conditioner is used to add moisture and heat to the feed mixture before pelleting. The conditioning process gelatinizes starches and improves the binding properties of the ingredients, resulting in higher-quality pellets.
- Temperature and Moisture Control: Effective conditioning requires precise control of temperature and moisture levels. Monitoring systems can be integrated to ensure that the feed mixture reaches the optimal conditions for pelleting.
5. Pelleting Equipment
The pelleting process is the heart of animal feed production, where the conditioned feed mixture is transformed into pellets.
- Pellet Mill: The pellet mill is the primary machine used for forming pellets from the feed mixture. It consists of a die and rollers that compress the mixture under high pressure. The type of pellet mill (e.g., ring die or flat die) can affect the quality and size of the pellets produced.
- Cooling System: After pelleting, the hot pellets must be cooled to reduce moisture content and prevent spoilage. A counterflow cooler is commonly used, allowing the pellets to cool down while minimizing the risk of damage.
6. Screening and Grading Equipment
Once the pellets are cooled, they need to be screened and graded to ensure uniformity and quality.
- Vibrating Screen: A vibrating screen is used to separate fines and oversized pellets from the desired product. This step ensures that only pellets of the correct size and quality proceed to packaging.
- Grading Equipment: Grading equipment can further classify the pellets based on size and quality, allowing for the production of different feed formulations tailored to specific livestock needs.
7. Packaging Equipment
The final step in the feed production process involves packaging the finished product for storage and distribution.
- Automatic Bagging Machine: An automatic bagging machine can efficiently fill, weigh, and seal bags of feed. This reduces manual labor and ensures accurate packaging, which is essential for inventory management.
- Bulk Loading Systems: For larger operations, bulk loading systems can be used to load feed directly into trucks or silos for transportation. This is particularly useful for large-scale distributors.
8. Control Systems
An effective control system is essential for monitoring and managing the entire production process.
- Programmable Logic Controllers (PLCs): PLCs are used to automate various processes within the feed production line, allowing for precise control over parameters such as feed rates, temperatures, and mixing times.
- Human-Machine Interfaces (HMIs): HMIs provide operators with a user-friendly interface to monitor and control the production process. They display real-time data on production metrics, allowing for quick adjustments and troubleshooting.
Conclusion
A 3-4 t/h animal feed production machine comprises several key pieces of equipment, each playing a vital role in the overall production process. From raw material reception and cleaning to grinding, mixing, conditioning, pelleting, screening, and packaging, each component contributes to the efficiency and quality of the final feed product.By investing in high-quality machinery and implementing effective control systems, feed manufacturers can optimize their production processes, reduce waste, and enhance the nutritional value of the feed produced. As the demand for animal feed continues to grow, understanding the main equipment of a 3-4 t/h feed production machine will be essential for maintaining a competitive edge in the market.