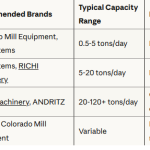
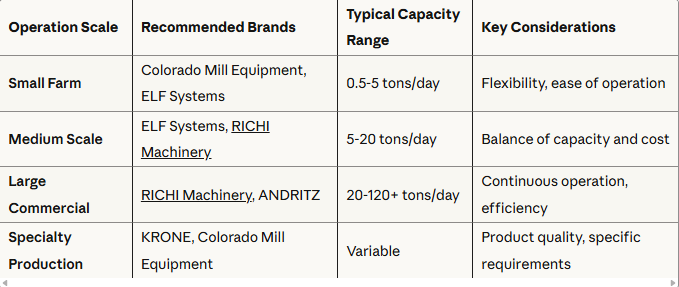
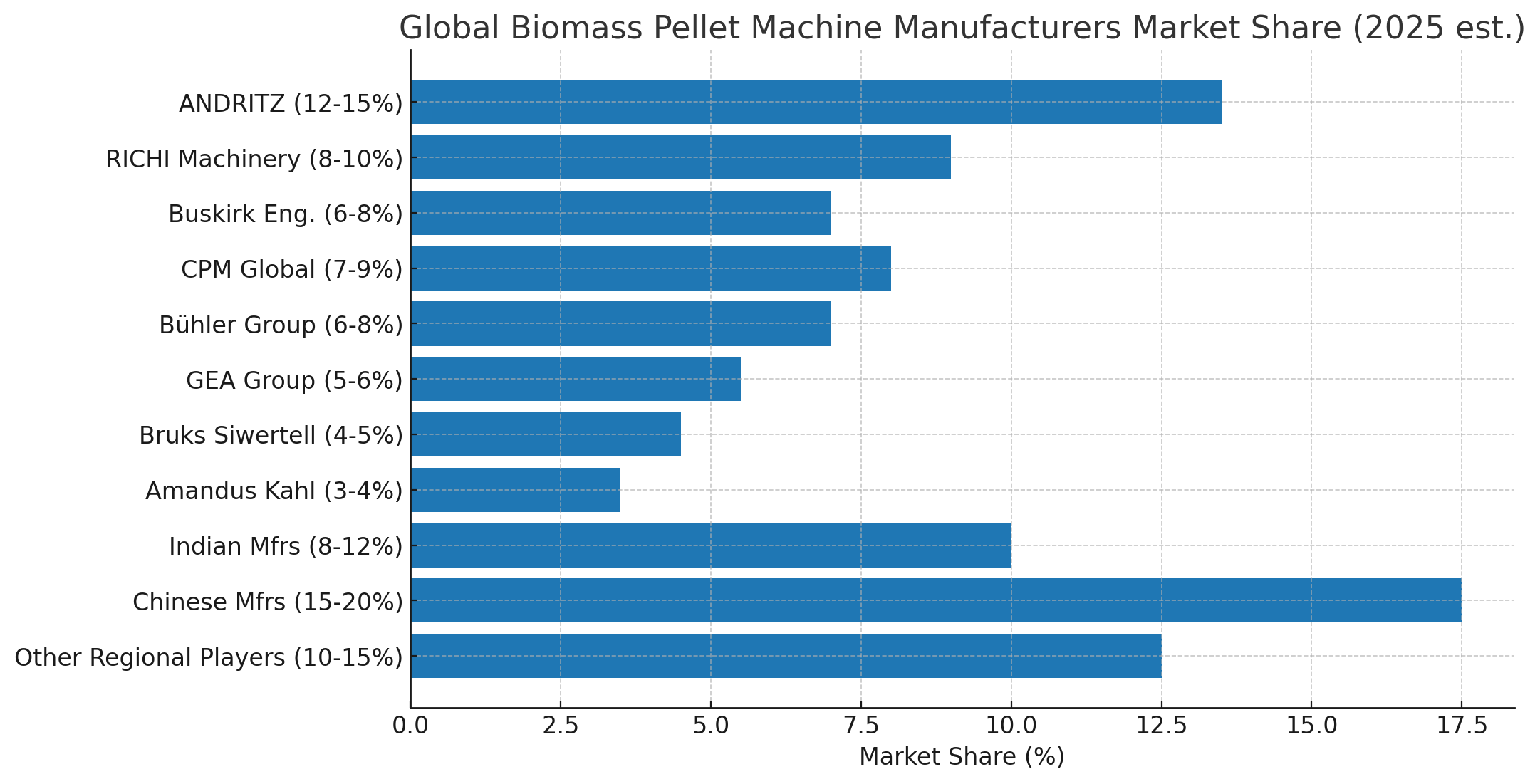
As Japan enhances its renewable energy sector, wood pellet plants are becoming more prevalent. However, these plants must adhere to stringent environmental standards to promote sustainability and minimize ecological impacts. Here’s an overview of the key environmental regulations and standards applicable to wood pellet plant in Japan:
Air Quality Regulations
- Air Pollution Control Act
- Regulations: This act governs air quality and requires wood pellet plants to comply with emission limits for:
- Particulate matter (PM)
- Nitrogen oxides (NOx)
- Sulfur oxides (SOx)
- Volatile organic compounds (VOCs)
- Monitoring: Plants must regularly monitor and report emissions, with specific limits based on plant size and location.
- Regulations: This act governs air quality and requires wood pellet plants to comply with emission limits for:
- Dioxin Control
- Standards: Japan has strict dioxin emission regulations. Plants must use best available technologies to minimize dioxin formation and release.
- Requirements: Regular testing and reporting of dioxin levels are mandatory.
Water Quality Standards
- Water Pollution Control Law
- Requirements: This law regulates wastewater discharge from industrial facilities, including wood pellet plants. Key requirements include:
- Treatment of wastewater before discharge
- Regular monitoring of water quality (e.g., pH, BOD, COD, and suspended solids)
- Proper management of stormwater runoff
- Requirements: This law regulates wastewater discharge from industrial facilities, including wood pellet plants. Key requirements include:
- Groundwater Protection
- Measures: Ensure prevention of groundwater contamination by using proper lining for storage areas and implementing spill prevention and control measures.
Waste Management
- Waste Management and Public Cleansing Law
- Requirements: This law covers waste handling, storage, and disposal. Wood pellet plants must:
- Classify and segregate waste streams
- Implement recycling programs
- Properly dispose of hazardous wastes
- Maintain detailed records of waste generation and disposal
- Requirements: This law covers waste handling, storage, and disposal. Wood pellet plants must:
- Biomass Ash Management
- Regulations: Specific regulations govern the handling and disposal of ash from biomass combustion. Options for ash utilization, such as soil amendments, should be explored and are subject to regulatory approval.
Noise and Vibration Control
- Noise Regulation Law
- Standards: Wood pellet plants must adhere to noise limits based on area type (e.g., residential, commercial). Measures may include:
- Installation of noise barriers
- Use of low-noise equipment
- Limiting operational hours in sensitive areas
- Standards: Wood pellet plants must adhere to noise limits based on area type (e.g., residential, commercial). Measures may include:
- Vibration Regulation Law
- Control: Vibration levels must be managed to avoid disturbances. This may involve:
- Proper foundation design
- Use of vibration dampening equipment
- Regular maintenance to prevent excessive vibration
- Control: Vibration levels must be managed to avoid disturbances. This may involve:
Energy Efficiency and Greenhouse Gas Emissions
- Energy Conservation Law
- Standards: Promote energy efficiency through:
- Implementation of energy-efficient technologies and processes
- Regular energy audits
- Setting and working towards energy reduction targets
- Standards: Promote energy efficiency through:
- Global Warming Countermeasures Law
- Requirements: Although biomass is carbon-neutral, plants must report greenhouse gas emissions and implement measures to minimize their carbon footprint.
Biodiversity and Ecosystem Protection
- Basic Act on Biodiversity
- Considerations: Requires consideration of biodiversity impacts. Wood pellet plants should:
- Assess potential impacts on local ecosystems
- Implement measures to protect sensitive habitats
- Consider sustainable sourcing of raw materials
- Considerations: Requires consideration of biodiversity impacts. Wood pellet plants should:
- Invasive Alien Species Act
- Precautions: Prevent introduction of invasive species through proper screening and treatment of imported biomass.
Environmental Impact Assessment
- Environmental Impact Assessment Law
- Process: Large-scale wood pellet plants may need to undergo a formal environmental impact assessment, involving:
- Detailed study of potential environmental impacts
- Public consultation and disclosure
- Development of mitigation measures
- Ongoing monitoring and reporting
- Process: Large-scale wood pellet plants may need to undergo a formal environmental impact assessment, involving:
Local Regulations and Zoning
- Local Requirements:
- Regulations: Compliance with local zoning restrictions, air and water quality standards, and specific industrial facility requirements is necessary. Early consultation with local authorities is crucial.
Sustainable Forestry Practices
- Forest and Forestry Basic Act
- Guidelines: Promote sustainable forest management practices. Wood pellet plants should:
- Source raw materials from sustainably managed forests
- Implement chain of custody systems to track wood sources
- Consider forest certification (e.g., FSC, PEFC)
- Guidelines: Promote sustainable forest management practices. Wood pellet plants should:
- Guidelines for Wood Biomass Utilization
- Standards: Provide recommendations for sustainable biomass sourcing and utilization, often required for plants receiving government subsidies or participating in the Feed-in Tariff (FIT) scheme.
Occupational Health and Safety
- Industrial Safety and Health Act
- Requirements: Focuses on preventing accidents and health hazards, including those with potential environmental impacts like dust explosions and chemical spills.
Continuous Improvement and Best Practices
- Recommendations:
- Systems: Implement environmental management systems (e.g., ISO 14001)
- Programs: Participate in voluntary environmental programs
- Engagement: Engage with local communities on environmental issues
- Innovation: Continuously improve environmental performance through technology upgrades and process optimization
Conclusion
Building and operating a wood pellet plant in Japan involves navigating a complex framework of environmental regulations and standards. These requirements cover air and water quality, waste management, noise and vibration control, energy efficiency, biodiversity protection, and more. Compliance with these standards ensures not only legal operation but also contributes to the overall sustainability of the biomass energy sector in Japan.
Prospective plant operators should engage early with regulatory authorities, environmental experts, and local communities to ensure adherence to all applicable standards. By doing so, they can support Japan’s renewable energy goals while minimizing ecological impact and fostering positive stakeholder relationships.
Related post: Wood Pellet Production Line