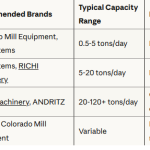
1. Introduction
In the modern agricultural industry, the production of organic fertilizers has gained significant momentum due to the increasing demand for sustainable and environmentally – friendly agricultural practices. Organic fertilizer pelletizers play a crucial role in the production process by transforming organic raw materials into granulated fertilizers. However, like many industrial equipment, organic fertilizer pelletizers consume a substantial amount of energy. High energy consumption not only increases production costs but also has a negative impact on the environment. Therefore, exploring effective energy – consumption optimization strategies for organic fertilizer pelletizers is of great significance for the sustainable development of the organic fertilizer industry.

2. Current Energy – Consumption Situation of Organic Fertilizer Pelletizers
2.1 Energy – Consumption Components
The energy consumption of organic fertilizer pellet making machines mainly comes from several aspects. First, the motor that drives the main working parts, such as the rollers in compression pelletizers or the screw in extrusion pelletizers, consumes a large amount of electrical energy. The continuous rotation of these components requires a significant power input to overcome the resistance from the organic raw materials during the granulation process. Second, the heating system, if any, also contributes to energy consumption. For example, in some cases where the raw materials need to be dried or pre – heated to an appropriate temperature for better granulation, the heating elements consume electrical or thermal energy. Third, auxiliary equipment such as conveyor belts and feeders also consume a certain amount of energy to transport the raw materials and the finished products.
2.2 Energy – Consumption Data Analysis
According to industry surveys and research, the energy consumption of organic fertilizer pelletizers varies depending on the type, size, and production capacity of the equipment. For a medium – sized compression pelletizer with a production capacity of 1 – 2 tons per hour, the power consumption of the main motor is usually in the range of 15 – 30 kW. Considering the continuous operation time, the daily energy consumption can be quite high. In addition, if the heating system is used, the energy consumption will increase significantly. For example, a simple electric heating system with a power of 5 – 10 kW may be required to dry the high – moisture raw materials, which further adds to the overall energy cost.
3. Factors Affecting Energy Consumption of Organic Fertilizer Pelletizers
3.1 Raw – Material Characteristics
Particle Size and Shape
The particle size and shape of the organic raw materials have a direct impact on the energy consumption of the pelletizer. If the raw materials have a large particle size, the pelletizer needs to consume more energy to break them down and form pellets. For example, in compression pelletization, large – sized raw – material particles may require higher pressure from the rollers to be forced through the die holes, resulting in increased energy consumption. Similarly, irregular – shaped raw – material particles may cause uneven stress distribution during the granulation process, making the equipment work less efficiently and consuming more energy. (Related solution: organic fertilizer processing plant)
Moisture Content
The moisture content of the raw materials is another critical factor. High – moisture raw materials are more difficult to granulate. In extrusion pelletization, if the moisture content of the raw materials is too high, the material may be too soft to form stable pellets, and the extruder may need to work harder to push the material through the die, increasing energy consumption. In addition, if the raw materials need to be dried to an appropriate moisture content before granulation, the drying process itself consumes a large amount of energy.
Chemical Composition
The chemical composition of the raw materials also affects energy consumption. Some raw materials with high fiber content, such as certain types of crop residues, may be more difficult to process and require more energy to be granulated. On the other hand, raw materials with a high content of easily – agglomerating substances may require less energy for granulation as they can form pellets more easily.
3.2 Equipment Design and Operation
Pelletizer Type
Different types of organic fertilizer pelletizers have different energy – consumption characteristics. Compression pelletizers generally require higher power for the compression process, especially when producing high – density pellets. Extrusion pelletizers, although they may have a relatively lower power consumption for the main driving motor in some cases, may consume more energy if the screw design is not optimized for the specific raw materials. Disc pelletizers usually consume less energy compared to compression and extrusion pelletizers, but their production capacity is also relatively lower.
Equipment Size and Capacity
Larger – sized and higher – capacity organic fertilizer pelletizers tend to consume more energy. However, the energy consumption per unit of product may not necessarily increase proportionally. Well – designed large – capacity equipment can achieve economies of scale in energy consumption. For example, a large – scale compression pelletizer with a production capacity of 5 – 10 tons per hour may have a more efficient power – transmission system and better – optimized working components, resulting in a lower energy consumption per ton of product compared to a small – scale pelletizer. (Related project:4T/H Organic Manure Production Plant In Japan)
Operation Parameters
The operation parameters of the pelletizer, such as the rotation speed of the rollers or the screw, the feed rate of the raw materials, and the pressure applied during granulation, also have a significant impact on energy consumption. An inappropriate rotation speed may cause the equipment to operate inefficiently, either over – or under – processing the raw materials and consuming more energy. A too – high feed rate may overload the equipment, leading to increased energy consumption and potential damage to the equipment. Similarly, incorrect pressure settings can affect the granulation quality and energy consumption.
4. Energy – Consumption Optimization Strategies
4.1 Raw – Material Pretreatment
Particle – Size Reduction
To reduce the energy consumption caused by large – sized raw – material particles, proper pretreatment methods such as shredding and grinding can be adopted. Using a shredder to break down large plant residues or chunks of manure into smaller particles can significantly reduce the resistance during the granulation process. After shredding, the raw materials can be further ground to an appropriate particle size using a grinder. This pretreatment not only improves the granulation effect but also reduces the energy required for the pelletizer to process the materials.
Moisture – Content Adjustment
Optimizing the moisture content of the raw materials is crucial for energy – consumption reduction. If the raw materials are too wet, drying methods such as natural drying in the sun, mechanical drying using a rotary dryer, or using a dehumidifier can be employed. However, these drying methods also consume energy. To balance the energy consumption, it is necessary to choose the most energy – efficient drying method according to the actual situation. For example, if the amount of raw materials is small, natural drying may be a cost – effective option. On the other hand, if the raw materials are too dry, adding an appropriate amount of water or a liquid binder can improve the granulation process and reduce energy consumption.
4.2 Equipment Optimization
Design Improvement
Innovative design of organic fertilizer pelletizers can lead to significant energy – consumption reduction. For compression pelletizers, improving the design of the rollers and dies can enhance the compression efficiency. Using advanced materials for the rollers and dies can reduce friction and wear, allowing the equipment to operate more smoothly and consume less energy. In extrusion pelletizers, optimizing the screw design, such as adjusting the pitch and diameter of the screw, can improve the material – conveying efficiency and reduce the energy required to push the raw materials through the die.
Upgrading of Components
Upgrading some key components of the pelletizer can also contribute to energy – consumption optimization. For example, replacing the traditional motors with high – efficiency motors can significantly reduce power consumption. High – efficiency motors have a higher power – factor and lower energy losses. In addition, using energy – saving bearings and seals can reduce the mechanical resistance in the equipment, further saving energy.
4.3 Operation – Parameter Optimization
Speed and Feed – Rate Adjustment
Finding the optimal rotation speed and feed rate is essential for reducing energy consumption. Through experimental research and data analysis, the appropriate rotation speed of the rollers or the screw can be determined according to the type and characteristics of the raw materials. A proper rotation speed can ensure that the raw materials are processed evenly and efficiently without over – or under – processing. Similarly, adjusting the feed rate to match the processing capacity of the pelletizer can prevent overloading and under – loading of the equipment, thereby reducing energy consumption.
Pressure Control
In compression pelletizers, precise pressure control is crucial. Using a pressure – sensing device to monitor and adjust the pressure applied during the granulation process can ensure that the pellets are formed with the appropriate density while minimizing energy consumption. If the pressure is too high, it will consume excessive energy; if the pressure is too low, the pellets may not have sufficient strength.
4.4 Energy – Recovery and Utilization
Heat – Recovery Systems
In cases where the granulation process involves heating, such as drying the raw materials, heat – recovery systems can be installed. For example, the hot exhaust gas from the dryer can be used to pre – heat the incoming raw materials or to heat the air in the production workshop. This way, the waste heat can be effectively recycled, reducing the overall energy consumption of the production process.
Kinetic – Energy Recovery
Some advanced organic fertilizer pelletizers can be equipped with kinetic – energy recovery devices. For example, during the braking process of the main motor or the conveyor belts, the kinetic energy can be converted into electrical energy and stored for later use. Although the amount of energy recovered in this way may be relatively small, it can still contribute to overall energy – consumption reduction in the long run.
5. Case Studies of Energy – Consumption Optimization
5.1 Case 1: A Medium – Sized Organic Fertilizer Plant
A medium – sized organic fertilizer plant in a certain region was facing high energy – consumption problems in its organic fertilizer pelletizer operation. The plant mainly used compost and manure as raw materials. After analyzing the raw – material characteristics, it was found that the raw materials had a relatively large particle size and high moisture content. The plant first installed a shredder and a grinder to reduce the particle size of the raw materials. Then, a rotary dryer was added to adjust the moisture content. In terms of equipment optimization, the plant replaced the old – fashioned compression – pelletizer motors with high – efficiency motors and improved the design of the rollers and dies. After implementing these measures, the energy consumption of the pelletizer decreased by about 20%, and the production efficiency also increased.
5.2 Case 2: A Small – Scale Family – Run Organic Fertilizer Production
A small – scale family – run organic fertilizer production mainly produced organic fertilizers for local farmers. The production used a small – sized disc pelletizer. The owner found that the energy consumption was relatively high due to improper operation parameters. Through testing and adjustment, the rotation speed of the disc was optimized, and the feed rate was adjusted according to the characteristics of the raw materials. In addition, the owner added a simple heat – recovery device by using a heat – exchanger to recycle the heat from the drying process of the raw materials. As a result, the energy consumption of the production decreased by about 15%, and the production cost was effectively reduced.
6. Conclusion
In conclusion, reducing the energy consumption of organic fertilizer pelletizers is an important measure to improve the economic and environmental benefits of the organic fertilizer industry. By understanding the current energy – consumption situation, analyzing the factors that affect energy consumption, and implementing effective energy – consumption optimization strategies such as raw – material pretreatment, equipment optimization, operation – parameter adjustment, and energy – recovery and utilization, significant energy savings can be achieved. Case studies have shown that these optimization strategies are practical and effective. In the future, with the continuous development of technology and the increasing awareness of energy conservation and environmental protection, more advanced energy – consumption optimization methods for organic fertilizer pelletizers are expected to emerge, promoting the sustainable development of the organic fertilizer industry.