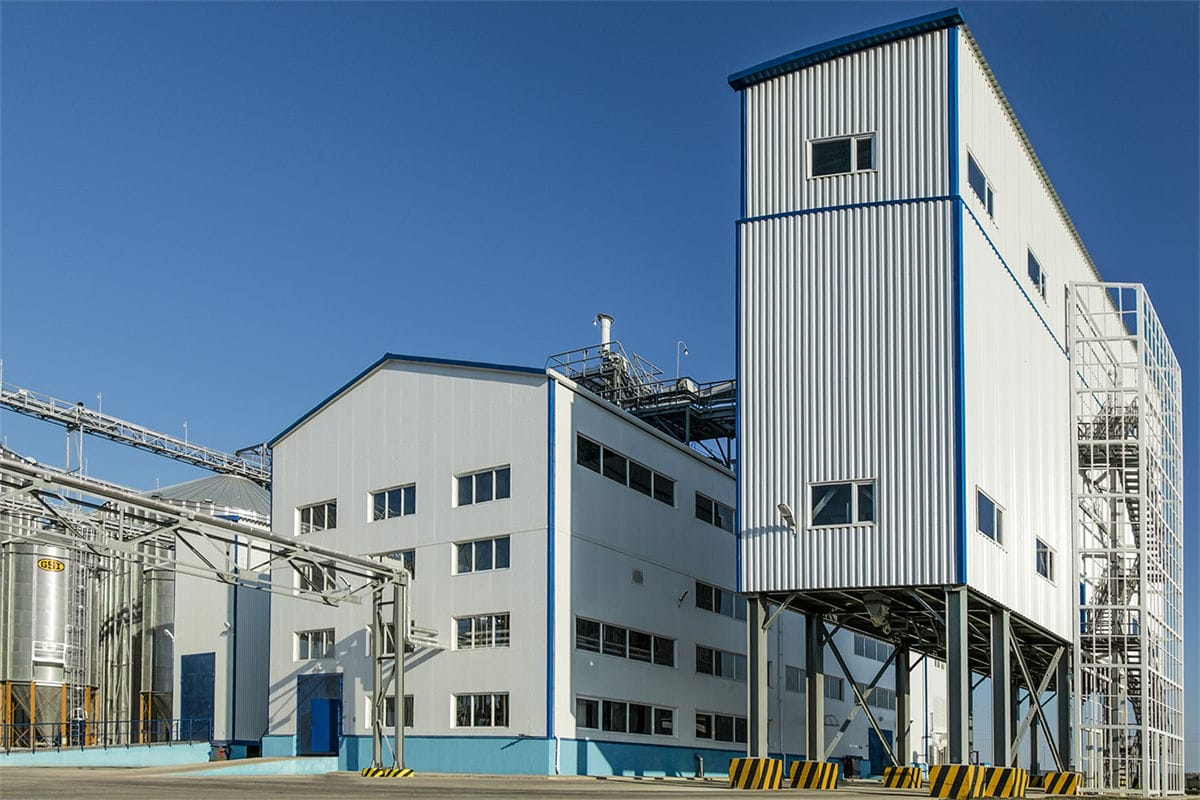
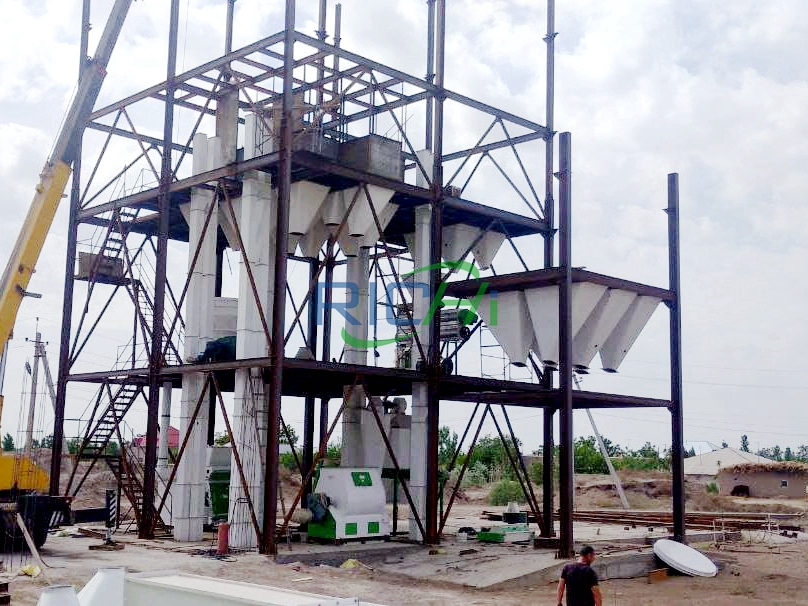
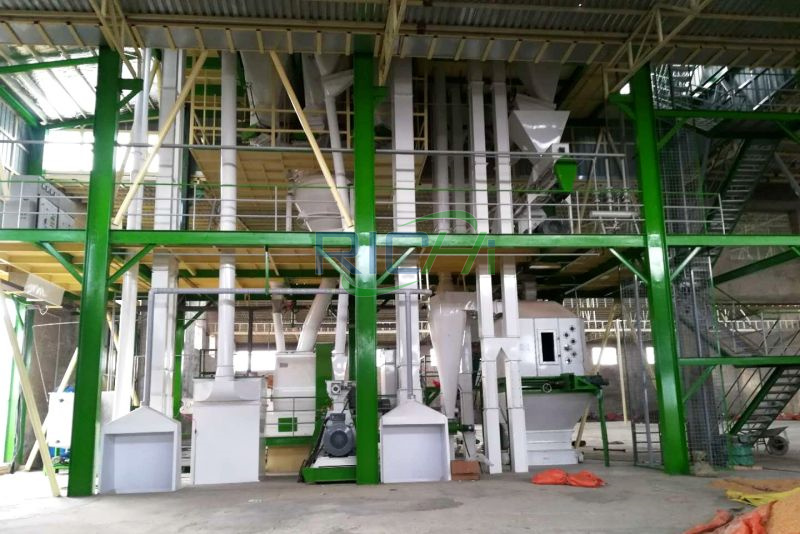
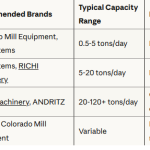
The design and layout of a poultry feed plant play a crucial role in ensuring efficient operations, maintaining product quality, and meeting the growing demand for poultry feed in Mexico’s thriving poultry industry. A well-planned layout not only enhances productivity but also ensures compliance with safety and quality standards. This article explores the key considerations and components of an optimal layout design for a poultry feed plant in Mexico.
Understanding the Mexican Context
Before delving into the specifics of layout design, it’s essential to consider the unique aspects of establishing a poultry feed plant in Mexico:
- Climate Considerations: Mexico’s diverse climate zones require careful planning for raw material storage and finished product handling.
- Regulatory Compliance: The layout must adhere to Mexican regulations regarding food safety, environmental protection, and worker safety.
- Local Raw Material Availability: Proximity to major grain-producing regions can influence the plant’s location and storage requirements.
- Market Demand: Understanding the distribution of poultry farms across Mexico can impact the plant’s location and production capacity.
Key Components of the Plant Layout
A well-designed poultry feed production line typically includes the following key areas:
- Raw Material Reception and Storage
- Grinding and Mixing Area
- Pelleting and Cooling Section
- Packaging and Warehousing
- Quality Control Laboratory
- Office and Administrative Area
- Maintenance Workshop
- Utilities and Services Section
Raw Material Reception and Storage
The layout should provide ample space for:
- Truck Weighbridge: For accurate measurement of incoming raw materials.
- Unloading Area: With sufficient space for multiple trucks to unload simultaneously.
- Storage Silos: For bulk ingredients like corn, soybean meal, and wheat.
- Warehouse: For storing bagged ingredients, micro-ingredients, and additives.
Design Considerations:
- Ensure easy access for delivery trucks.
- Implement dust control systems to maintain air quality.
- Design for proper ventilation to prevent moisture accumulation.
Grinding and Mixing Area
This area is the heart of the feed production process and should include:
- Grinding Equipment: Hammer mills or roller mills for size reduction of grains.
- Batching System: For precise weighing and proportioning of ingredients.
- Mixing Equipment: Horizontal or vertical mixers for homogeneous blending.
Design Considerations:
- Arrange equipment to minimize material transport distances.
- Implement sound insulation to reduce noise levels.
- Ensure adequate space for maintenance and cleaning activities.
Pelleting and Cooling Section
For plants producing pelleted feed, this area should include:
- Conditioner: For steam conditioning of mash feed.
- Pellet Mill: For compressing feed into pellets.
- Cooler: To reduce pellet temperature and moisture content.
- Crumbler: For producing crumbles (if required).
Design Considerations:
- Ensure proper ventilation to manage heat and moisture.
- Design for easy cleaning and maintenance access.
- Implement dust collection systems to maintain air quality.
Packaging and Warehousing
This area should accommodate:
- Packaging Lines: For bagging finished feed products.
- Palletizing Area: For efficient stacking and storage.
- Finished Product Warehouse: With proper ventilation and pest control measures.
Design Considerations:
- Ensure smooth flow from production to packaging to storage.
- Design for easy truck loading for product distribution.
- Implement inventory management systems for efficient stock control.
Quality Control Laboratory
A well-equipped laboratory is essential for ensuring feed quality and safety:
- Sample Collection Points: Throughout the production process.
- Testing Equipment: For nutrient analysis, microbial testing, and physical quality checks.
Design Considerations:
- Locate the lab centrally for easy access from all production areas.
- Ensure proper isolation from production areas to maintain a clean environment.
Office and Administrative Area
This area should include:
- Management Offices
- Meeting Rooms
- Employee Facilities: Lockers, restrooms, and break areas.
Design Considerations:
- Position offices with a clear view of production areas for effective supervision.
- Ensure proper sound insulation from production noise.
Maintenance Workshop
A dedicated area for equipment maintenance and repair:
- Tool Storage
- Spare Parts Inventory
- Repair Stations
Design Considerations:
- Locate centrally for easy access to all production areas.
- Ensure adequate ventilation and safety equipment.
Utilities and Services Section
This area should house:
- Boiler Room: For steam generation.
- Electrical Control Room
- Water Treatment Facility
- Compressed Air System
Design Considerations:
- Ensure easy access for maintenance and emergency situations.
- Implement proper safety measures and containment systems.
Optimizing Material Flow
The layout should be designed to optimize material flow through the plant:
- Implement a logical sequence from raw material reception to finished product storage.
- Minimize cross-traffic and backtracking of materials.
- Use gravity flow where possible to reduce energy consumption.
Safety and Environmental Considerations
The layout must prioritize safety and environmental protection:
- Design wide aisles and clear pathways for safe movement of personnel and equipment.
- Implement dust control systems throughout the plant.
- Design for proper waste management and recycling.
- Ensure compliance with Mexican environmental regulations.
Future Expansion Considerations
When designing the layout, consider potential future expansion:
- Allow space for additional storage silos or warehousing.
- Design production areas with the possibility of adding new processing lines.
- Ensure utilities and services can accommodate increased capacity.
Conclusion
Designing an optimal layout for a poultry feed plant in Mexico requires careful consideration of various factors, from local climate and regulations to efficient material flow and future expansion possibilities. By focusing on these key elements and tailoring the design to the specific needs of the Mexican market, it’s possible to create a highly efficient, safe, and quality-focused poultry feed production facility.
The success of the plant will ultimately depend on how well the layout facilitates smooth operations, maintains product quality, and adapts to the evolving needs of Mexico’s dynamic poultry industry. Regular review and optimization of the layout will ensure the plant remains competitive and efficient in the long term.