In the ever-evolving landscape of renewable energy solutions, the demand for fuel pellets has witnessed a remarkable surge. Fuel pellets, typically made from compressed biomass materials such as wood waste, agricultural residues, or energy crops, offer a sustainable and carbon-neutral alternative to traditional fossil fuels. As the world continues to embrace greener energy sources, the construction of fuel pellet plants has become a crucial endeavor.
When it comes to building a 1-10t/h fuel pellet plant, a range of critical factors must be carefully considered to ensure efficient operations, profitability, and long-term sustainability. From feedstock sourcing and equipment selection to regulatory compliance and environmental impact, each aspect plays a pivotal role in the success of the plant.
Feedstock Availability and Quality
The availability and quality of feedstock are paramount considerations when building a fuel pellet plant. A reliable and consistent supply of biomass materials is essential to maintain uninterrupted production and meet the plant’s capacity requirements. Conducting a thorough assessment of local and regional feedstock sources, such as sawmills, agricultural operations, or dedicated energy crop plantations, is crucial.Additionally, the quality of the feedstock must be evaluated to ensure it meets the necessary specifications for pellet production. Factors such as moisture content, particle size, and contaminant levels can significantly impact the efficiency of the pelleting process and the quality of the final product.
Related post: https://www.richipelletmachine.com/wood-pellet-mill/
Plant Location and Infrastructure
Selecting the optimal location for the fuel pellet plant is a critical decision that can influence operational costs, logistics, and environmental impact. Proximity to feedstock sources, transportation networks, and potential customers should be carefully considered to minimize transportation costs and carbon footprint.Furthermore, the availability of necessary infrastructure, such as access to utilities (water, electricity, and natural gas), waste management facilities, and skilled labor, should be thoroughly evaluated. Ensuring adequate infrastructure can streamline operations and reduce the need for costly upgrades or modifications during the construction phase.
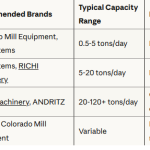
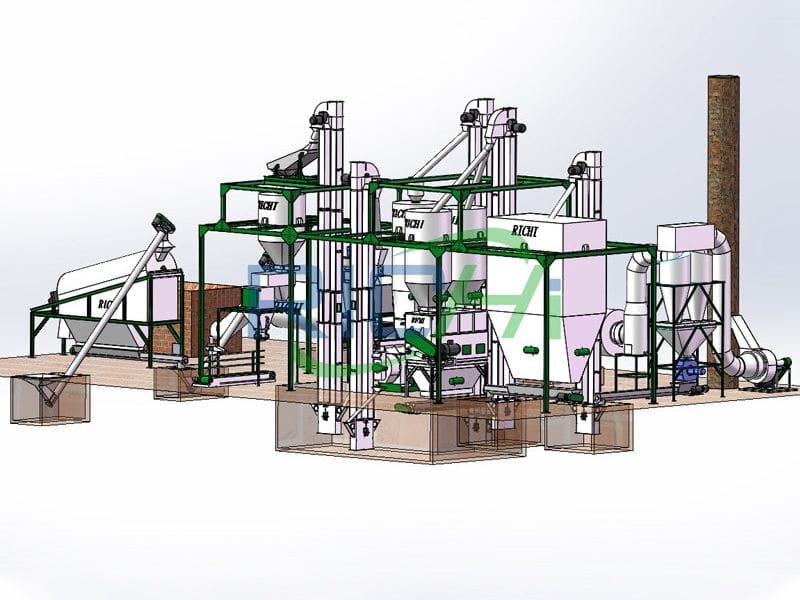
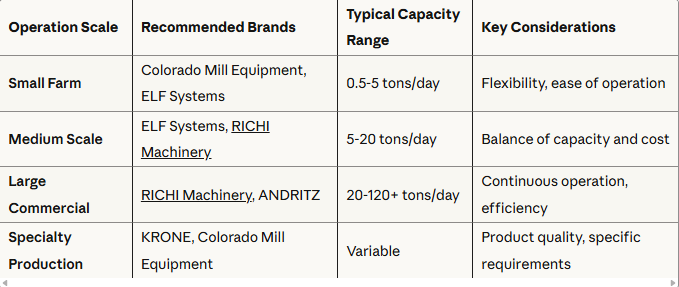
Equipment Selection and Layout
The selection of appropriate equipment and the efficient layout of the plant are essential for maximizing productivity and minimizing operational costs. When building a 1-10t/h fuel pellet plant, key equipment considerations include:
- Feedstock handling and pre-processing systems
- Drying and conditioning systems
- Pellet mills and associated components
- Cooling and screening systems
- Packaging and storage facilities
Choosing high-quality, energy-efficient equipment from reputable manufacturers can ensure reliable performance, reduce maintenance costs, and contribute to the overall sustainability of the plant. Additionally, optimizing the layout of the equipment and material flow can enhance efficiency, minimize bottlenecks, and improve worker safety.
Environmental Impact and Regulatory Compliance
Fuel pellet plants are subject to various environmental regulations and permitting requirements, which must be carefully considered during the planning and construction phases. Conducting comprehensive environmental impact assessments and obtaining necessary permits and approvals are crucial to ensure compliance and avoid potential legal and financial consequences.Key areas of focus include air emissions, water usage and discharge, noise pollution, and waste management. Implementing appropriate mitigation strategies, such as air pollution control systems, water treatment facilities, and waste recycling programs, can help minimize the plant’s environmental footprint and ensure regulatory compliance.
Energy Efficiency and Sustainability
Building a fuel pellet plant with energy efficiency and sustainability in mind can significantly reduce operational costs and environmental impact. Incorporating energy-efficient technologies, such as heat recovery systems, variable frequency drives, and renewable energy sources (e.g., solar or wind power), can optimize energy consumption and reduce reliance on fossil fuels.Additionally, implementing sustainable practices throughout the plant’s operations, such as water conservation measures, waste minimization strategies, and responsible sourcing of feedstock, can contribute to the overall sustainability of the facility and align with the principles of a circular economy.
Safety and Risk Management
Ensuring the safety of workers and minimizing potential risks are paramount considerations when building a fuel pellet plant. Conducting comprehensive risk assessments and implementing robust safety protocols, training programs, and emergency response plans are essential.Key areas of focus include fire and explosion prevention, dust control measures, proper handling and storage of hazardous materials, and adherence to occupational health and safety regulations. Investing in appropriate safety equipment, such as fire suppression systems, personal protective equipment, and monitoring devices, can help mitigate risks and create a safe working environment.
Financial Planning and Feasibility Analysis
Building a fuel pellet plant requires significant capital investment, making financial planning and feasibility analysis critical components of the project. Conducting a thorough feasibility study, including market analysis, cost projections, and return on investment calculations, can help assess the viability of the project and secure necessary funding.Additionally, exploring potential financing options, such as loans, grants, or partnerships, can provide the necessary resources to support the construction and initial operations of the plant. Developing a comprehensive business plan and financial projections can also attract investors and stakeholders, ensuring the long-term success of the venture.By carefully considering these key issues and implementing best practices, stakeholders can successfully navigate the complexities of building a 1-10t/h fuel pellet plant. Addressing feedstock availability, plant location, equipment selection, environmental impact, energy efficiency, safety, and financial planning will not only contribute to the plant’s operational success but also support the broader transition towards a more sustainable and renewable energy future.